Cannabis cultivation, whether indoors or outdoors, is often challenged by various pests that can threaten the health and yield of the plants. Effective pest control strategies are essential to ensure the success of cannabis crops and maintain product quality. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into common cannabis pests, pest management laws, the creation of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programs, popular pesticides, banned substances, regional regulations, beneficial organisms, and practical pest control methods.
AI-Generated image
Understanding Common Cannabis Pests:
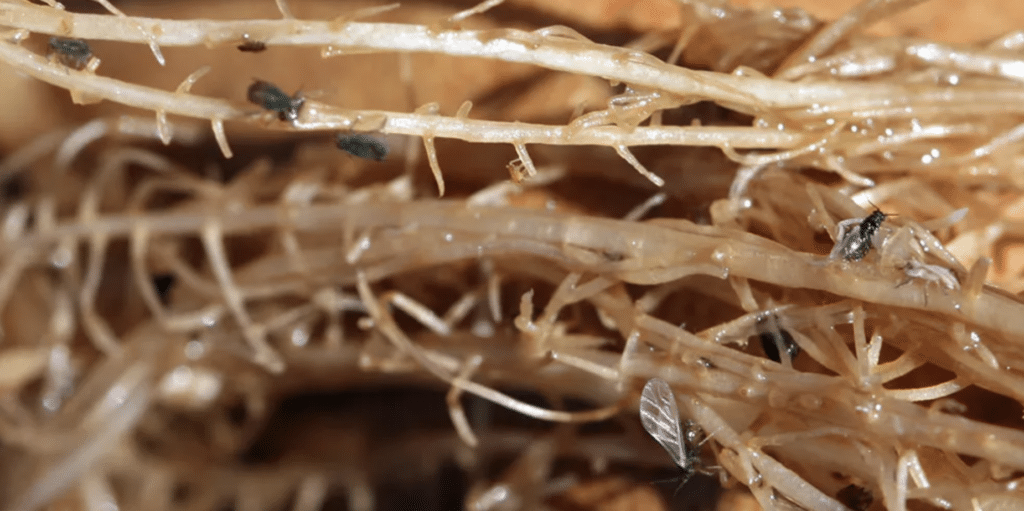
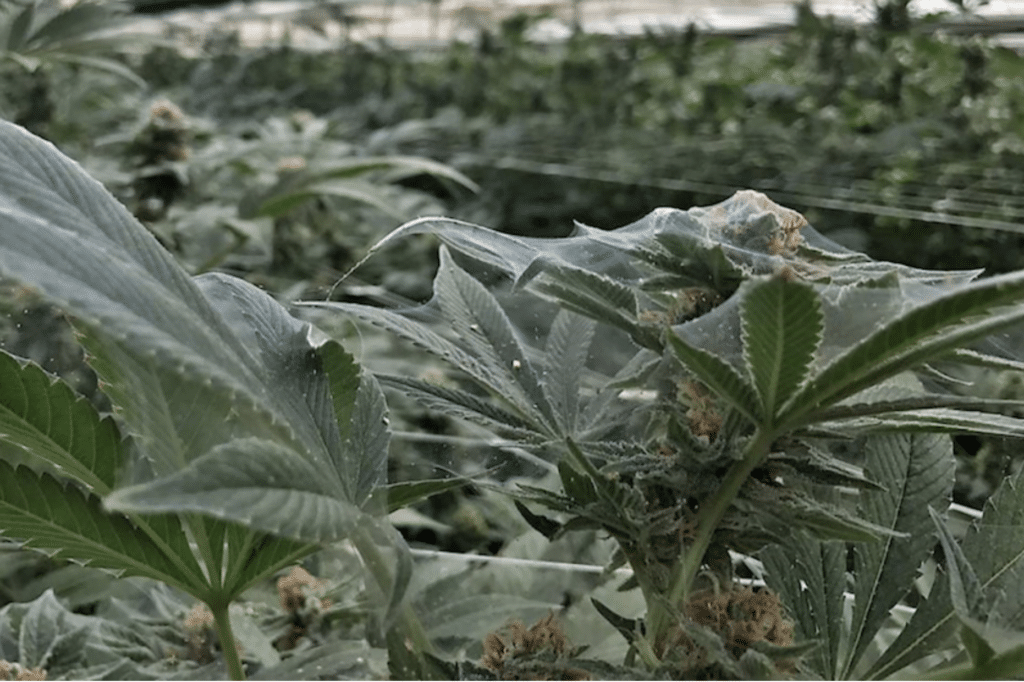
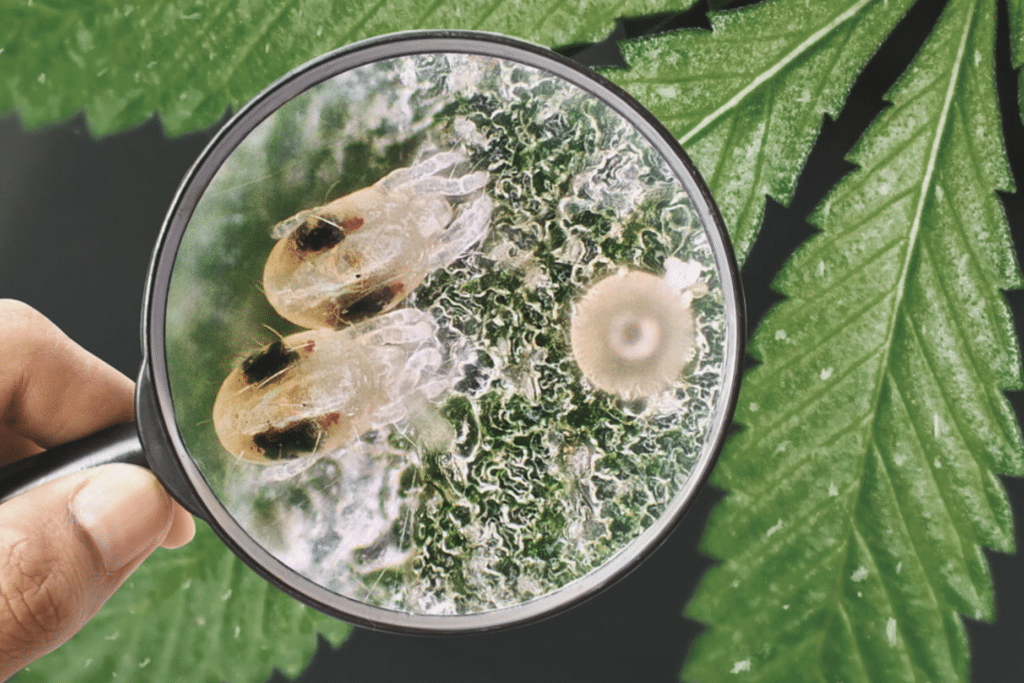
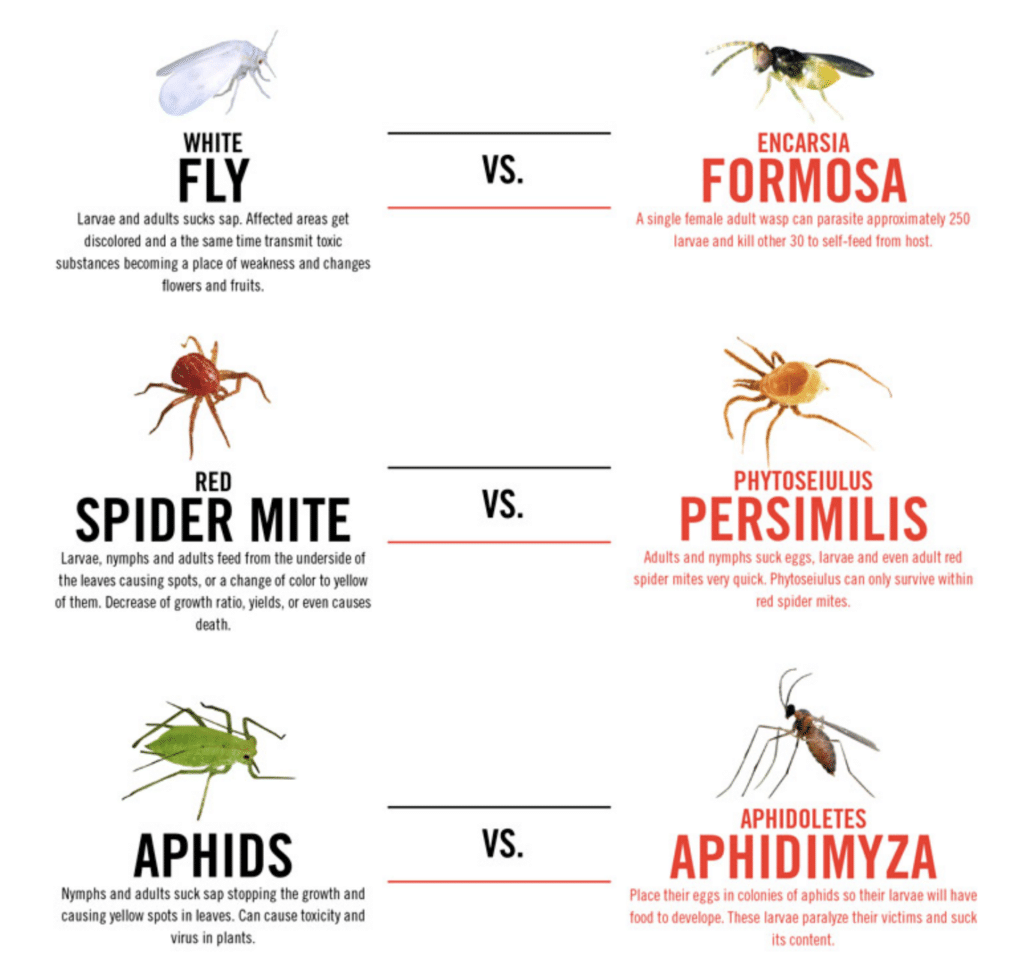
Common pests in cannabis cultivation include spider mites, aphids, thrips, fungus gnats, whiteflies, mealybugs, scale insects, caterpillars, leafhoppers, root aphids, broad mites, russet mites, springtails, leaf miners, and root-knot nematodes. Each pest presents unique challenges and requires specific control measures to mitigate their impact on cannabis plants.
List of popular pests in cannabis:
- Spider Mites
- Aphids
- Thrips
- Fungus Gnats
- Whiteflies
- Mealybugs
- Scale Insects
- Caterpillars
- Leafhoppers
- Root Aphids
- Broad Mites
- Russet Mites
- Springtails
- Leaf Miners
- Root Knot nematodes
Effective Pest Management Laws and Regulations:
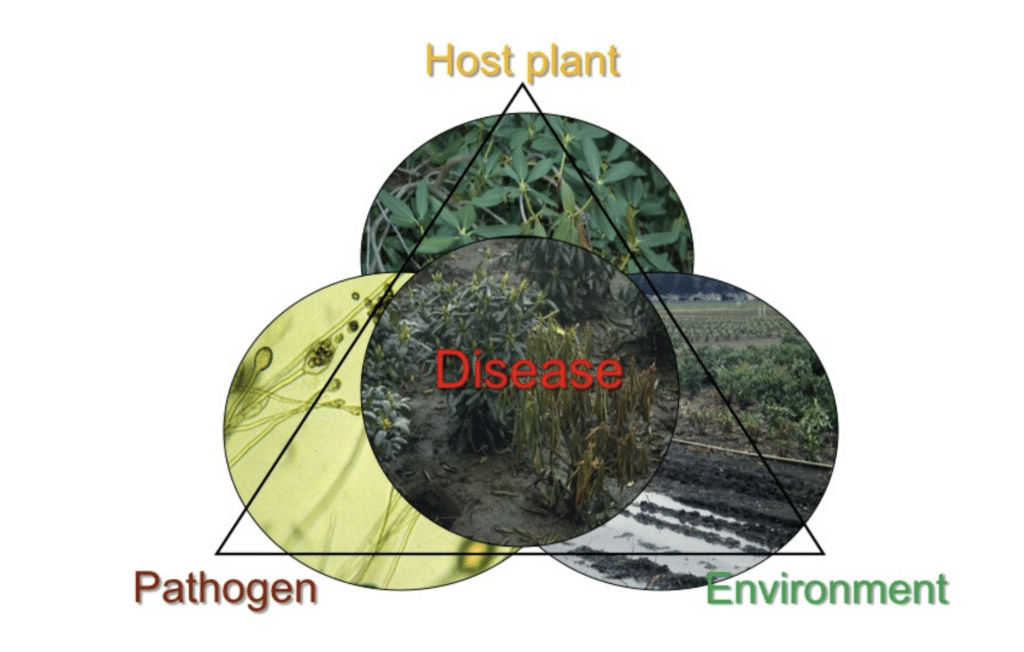
It is crucial for cannabis growers to adhere to pest management laws and regulations to ensure compliance with environmental and safety standards. Regional regulations play a significant role in determining permissible pesticides and pest control practices. Familiarizing oneself with local laws and guidelines is essential for sustainable and responsible cannabis cultivation.
Creating an Integrated Pest Management Program:
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention, monitoring, and control using a combination of biological, cultural, physical, and chemical methods. By integrating multiple strategies, growers can minimize pesticide use while effectively managing pests. Resources such as educational materials and online tutorials can assist growers in developing customized IPM programs tailored to their specific growing conditions and pest pressures.
Popular Pesticides for Cannabis Cultivation:
A variety of pesticides are commonly used in cannabis cultivation, including neem oil, azadirachtin, pyrethrins, spinosad, insecticidal soap, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), horticultural oil, sulfur, diatomaceous earth, and beneficial fungi such as Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae. These pesticides offer different modes of action and can be used in rotation to prevent pest resistance and minimize environmental impact.
List of popular pesticides:
- Neem oil
- Azadirachtin
- Pyrethrins
- Spinosad
- Insecticidal soap
- Potassium salts of fatty acids (also known as insecticidal soap)
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt)
- Horticultural oil
- Sulfur
- Diatomaceous earth
- Beauveria bassiana (a beneficial fungus)
- Metarhizium anisopliae (a beneficial fungus)
- Rosemary oil
- Peppermint oil
- Garlic oil
- Cinnamon oil
- Thyme oil
- Citrus oil
- Geraniol
- Eugenol
- Cinnamaldehyde
- Capsaicin
- Garlic extract
- Clove oil
- Thyme extract
Understanding Banned Substances:
Certain pesticides, old standbys such as Forbid, Merit, Floramite, and Avid, are effective but banned due to their negative environmental or human health impacts. The use of these chemicals can result in failed test results, fines, and mandated destruction of products. Growers must prioritize the use of approved pesticides and adopt alternative pest control methods to ensure compliance with regulations and protect the environment.
Banned substances:
Forbid, Merit, Floramite, and Avid work great but they are not allowed due to negative environmental or human impact. These chemicals are long-lasting and cause failed test results, fines, and mandated destruction of products.
Beneficial Organisms and their Challenges:
Beneficial organisms, such as predatory insects and beneficial bacteria, can play a crucial role in biological pest control. However, they also pose challenges in indoor cultivation, including the need for constant monitoring, the risk of contamination, and the requirement for suitable environmental conditions. While beneficial organisms can be effective, growers must carefully manage their introduction and ensure proper environmental support to maximize their impact.
Practical Pest Control Methods:
Positive identification of pests is essential for selecting the most appropriate control methods. Mechanical and physical removal, such as handpicking or pruning affected plant parts, can be effective for managing certain pests. Biological control involves the use of natural predators or beneficial organisms to suppress pest populations. Chemical application should be used as a last resort and applied judiciously to minimize risks to human health and the environment.
Conclusion:
Effective pest control is paramount for successful cannabis cultivation. By understanding common pests, adhering to pest management laws, creating IPM programs, using approved pesticides, avoiding banned substances, considering regional regulations, utilizing beneficial organisms, and implementing practical control methods, growers can protect their crops and ensure a high-quality yield. Continued education, research, and collaboration within the cannabis community are essential for advancing sustainable and responsible pest management practices in the industry.
For further resource mining try: Experienced cultivators, Suzanne Wainwright Evans, pest-specific white papers, and local entomologists.
Additional resources:
Common pests study
Creating an IPM program video